Created by: Edda Valdimarsdóttir Blumenstein
In this article, you will read about how to Extract-Refresh Data Sources for Tableau Online, in exMon. This provides better insight into the refreshes and more control over the refresh schedule.
Extract Refresh in exMon
- Start by saving the following python scripts to the C: drive
- Name of script: Refresh_tableau_online_extract.py
import sys
import argparse
from API_Handler import APIHandler
# ----------------------------------------------------
# ----------------------------------------------------
# ----------------------------------------------------
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Bakvordur Datapump')
parser.add_argument('--server', required=True, help='Type of .')
parser.add_argument('--site_name', required=True, help='Type of .')
parser.add_argument('--user', required=False, default = None, help='Type of .')
parser.add_argument('--pw', required=False, default = None, help='Type of .')
parser.add_argument('--personal_access_token_name', required=False, default = None, help='Type of .')
parser.add_argument('--personal_access_token_secret', required=False, default = None, help='Type of .')
parser.add_argument('--datasource', required=True, help='Type of .')
args = parser.parse_args()
pumpConfig = {}
pumpConfig['server'] = args.server
pumpConfig['site_name'] = args.site_name
pumpConfig['user'] = args.user
pumpConfig['pw'] = args.pw
pumpConfig['personal_access_token_name'] = args.personal_access_token_name
pumpConfig['personal_access_token_secret'] = args.personal_access_token_secret
pumpConfig['datasource'] = args.datasource
# ----------------------------------------------------
# ----------------------------------------------------
# ----------------------------------------------------
apiHan_refresh = APIHandler(pumpConfig['server'], pumpConfig['site_name'], pumpConfig['user'], pumpConfig['pw'], pumpConfig['personal_access_token_name'], pumpConfig['personal_access_token_secret'], pumpConfig['datasource'])
test = apiHan_refresh.RunRefresh()
temp = ''Name of script: API_Handler.py
from sys import exec_prefix
import requests
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import time
import datetime
import logging
import tableauserverclient as TSC
from tableauserverclient.server.endpoint.workbooks_endpoint import Workbooks
class APIHandler(object):
def __init__(self, server, site_name, user, pw, personal_access_token_name, personal_access_token_secret, datasource):
self.server = server
self.site_name = site_name
self.user = user
self.pw = pw
self.personal_access_token_name = personal_access_token_name
self.personal_access_token_secret = personal_access_token_secret
self.datasource = datasource
self.Initialize()
def Initialize(self):
try:
if self.user is 'None' and self.pw is 'None':
tableau_auth = TSC.PersonalAccessTokenAuth(self.personal_access_token_name, self.personal_access_token_secret, site_id=self.site_name)
self.server = TSC.Server(self.server, use_server_version=True)
self.server.auth.sign_in(tableau_auth)
print('Signed in with Token.')
elif self.personal_access_token_name is 'None' and self.personal_access_token_name is 'None':
tableau_auth = TSC.TableauAuth(self.user, self.pw, site_id=self.site_name)
self.server = TSC.Server(self.server, use_server_version=True)
self.server.auth.sign_in(tableau_auth)
print('Signed in with user name')
except Exception as e:
print('Initialization failed with error: ' + str(e))
exit(1)
def RunRefresh(self):
all_datasources, pagination_item = self.server.datasources.get()
for dSource in all_datasources:
if dSource.name == self.datasource:
try:
datasource = self.server.datasources.get_by_id(dSource.id)
refreshed_datasource = self.server.datasources.refresh(datasource)
self.HandleRefreshWait(refreshed_datasource.id)
except Exception as e:
print('Refresh failed with error: ' + str(e))
exit(1)
def HandleRefreshWait(self, jobId):
complete_time = None
counter = 0
started = False
sleep_timer = 10
while complete_time is None:
extract = self.server.jobs.get_by_id(jobId)
if str(extract._finish_code) == "0":
complete_time = (extract._completed_at).strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
else:
if extract.started_at is None:
print("Refresh has not started.")
else:
if started == False:
print("Refresh started at " + (extract._started_at).strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') + '.')
started = True
if counter == 0:
print("Refresh is running.")
else:
print("Refresh is still running.")
counter += 1
if complete_time is None:
time.sleep(sleep_timer)
refresh_time = counter*sleep_timer
Next steps
- Create a Package for the refresh extract for the data source. It is necessary to create a package for each data source.
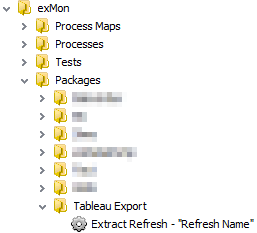
- In the extract refresh package put the following information in the Production - PROD command
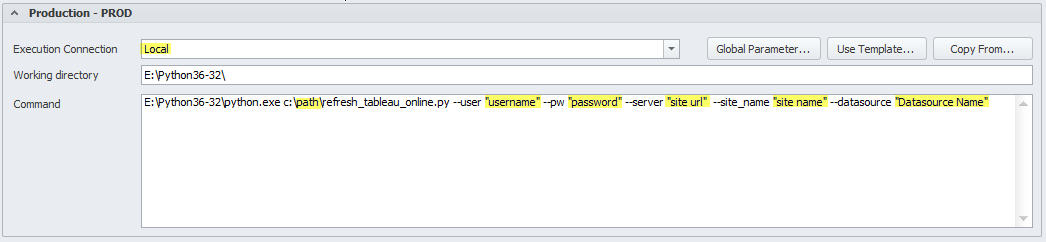
- Using username and password:
- Using personal access token
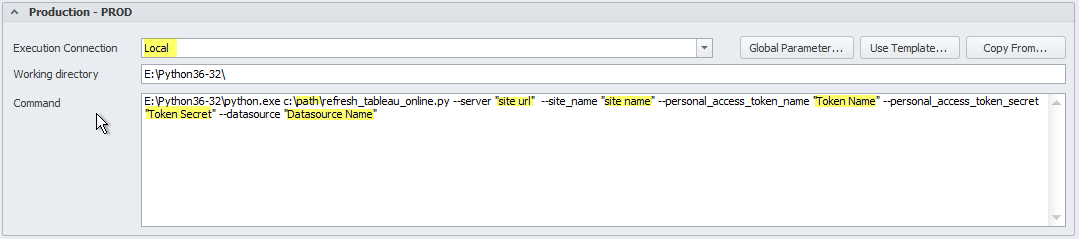
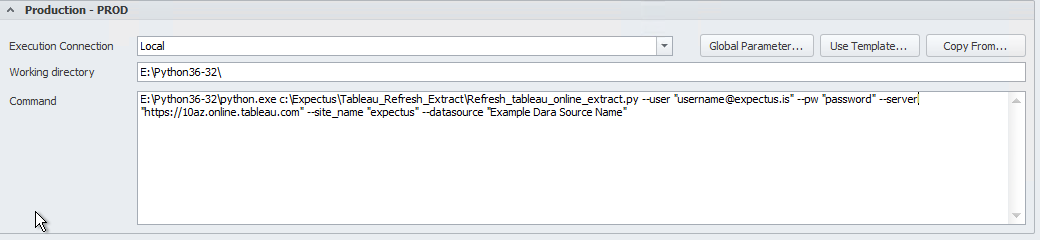
- Identify the Execution Connection
- Establish the location of the python script in the command window. The highlighted parameters that can be determined in the Tableau online server.
Note: We highly recommend using Global Parameter to hide the password used in the command window for increased security
Execution Example
- site url and site name
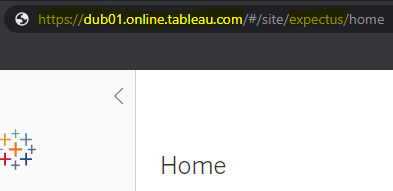
- Using username and password to sign into the tableau online server
- Username and Password
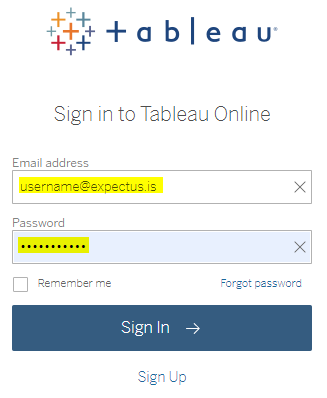
- Personal Access Token Name and Personal Access Token Secret
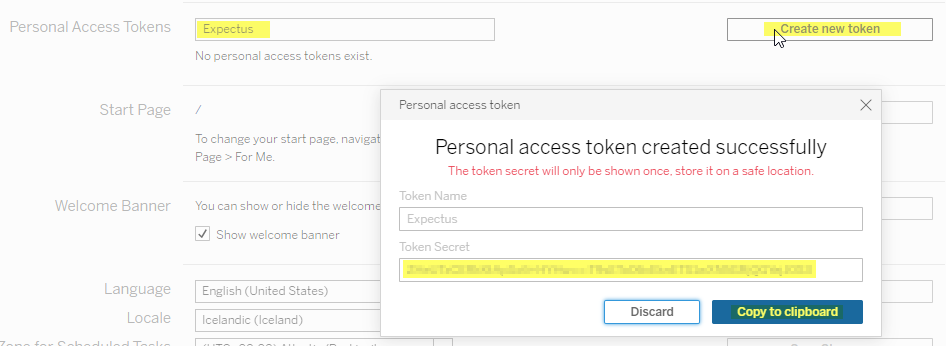
Create access token
In this section, you will learn how to create an access token for the tableau online server.
- Name the Personal Access Token
- 'Create New Token'
- Copy the Personal Access Token Secret
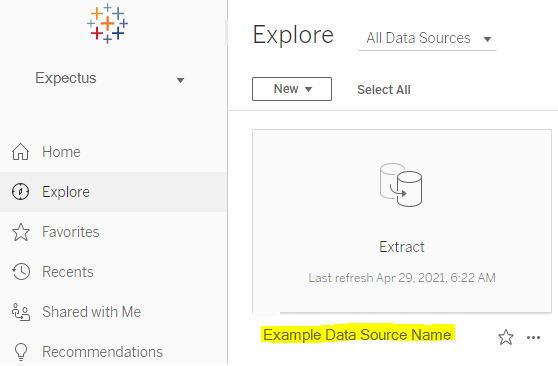
Data source name:
In the Tableau online server the name of the data source can be identified
Given that the python scripts have been located in C:\location\ the command for the Extract Refresh package will be as follows:
Signing in with username and password
Signing in with Personal Access Token
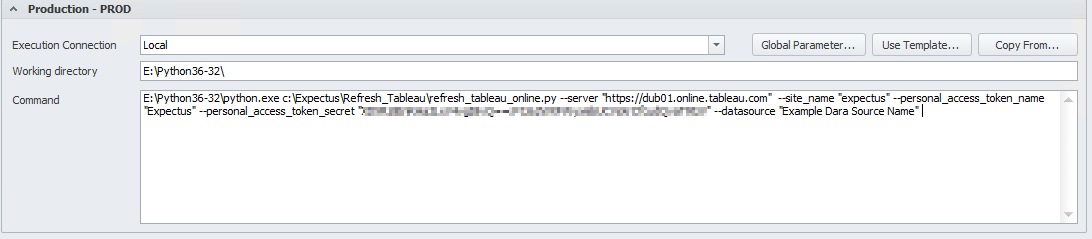
Finally, save and deploy the package.
Command to copy.
Working directory: E:\Python36-32\
Command: E:\Python36-32\python.exe c:\path\refresh_tableau_online.py --user "username" --pw "password" --server "site url" --site_name "site name" --personal_access_token_name "Token Name" --personal_access_token_secret "Token Secret" --datasource "Datasource Name"
Edda is the author of this solution article.
